Many organisations may have well defined security policies and processes in place. Processes that respond to vulnerabilities, alerts, and other security gaps in their network and software infrastructure.
But these practices often don’t extend to newer technologies such as cloud and virtual infrastructure which is so prevalent in today’s workplace.
Brinqa – the background

Brinqa connects and synchronises siloed cybersecurity products, processes and teams. With the goal of reducing cyber-risk and improving an organisation’s cybersecurity posture.
The Brinqa platform focuses on the modelling, analysis, prioritisation, remediation and reporting of cyber-risk.
With integrations to 150+ security and business data sources, it can deliver a knowledge-driven and risk-centric approach to managing security posture.
Enterprise benefits of Brinqa
- Visibility across all vulnerability risk in one place
- Faster risk identification saves time and money
- Automated from scan to ticket creation
- Tickets only closed when verified by scanner
- Prioritises remediation to address the most exploited and prevalent vulnerabilities
- Improve compliance and reduce risk of fines
Read our Brinqa case studies.
Brinqa “Knowledge Graph”
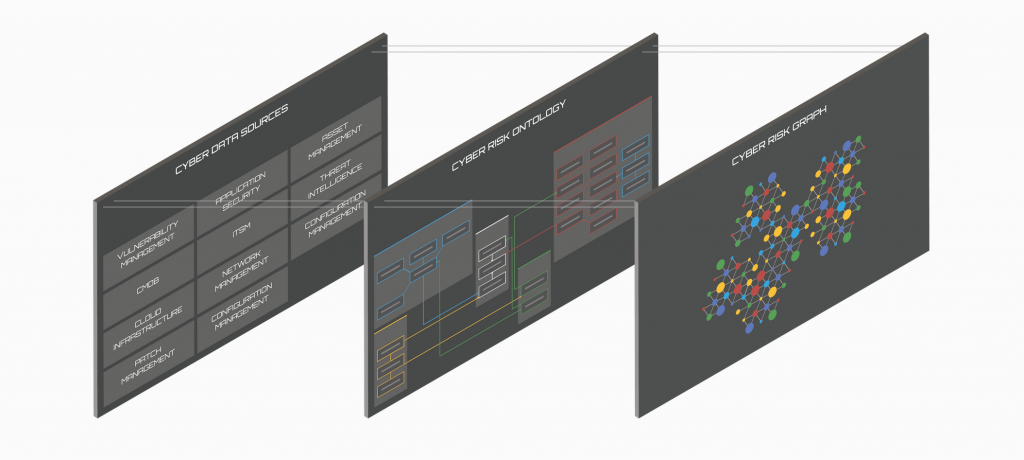
The Brinqa Knowledge Graph integrates the various data sources into a single source of truth, utilised by different stakeholders.
It connects all relevant security and business data, establishes a common risk language, and powers cybersecurity insights and outcomes with large customers with several million assets.
The result is a consistent understanding of assets that factor into determining their associated risk. Providing better knowledge of their risk posture based on accurate asset information.
It offers the ability to deprioritise false positives while highlighting the most critical risks for remediation.
Request a live Brinqa demo.
Reducing cyber-risk and improving cybersecurity posture
It’s dangerous to make compliance the primary driver for cyber-risk management goals and strategies. It is possible to be legally compliant but still be at serious risk from a cybersecurity perspective.
For example, say you turn on the compliance report which states that you complied with four out of five requirements. What about the 5th requirement that you failed? Should you follow up on that?
To be effective, enterprise cyber risk management must be a continuous, consistent process that brings together people and information across business, IT and information security.
For more on how to assess your security posture, read our blog: Assess your security Posture with our Security Maturity Model.
Understanding Enterprise Cyber-Risks
CISOs tend to look at risk in terms of digital assets, threats to destroy data and software or disrupt networks. However, enterprise cyber-risks are far more extensive in nature.
Examples include:
- Diminished brand reputation caused by customers’ confidential information being compromised.
- Physical damage or even fatalities caused by hacking operational technology (OT) systems.
- Financial losses due to critical business applications being unavailable as a result of DDoS attacks.
To learn more about the difference between Vulnerability Scanning and Pen testing read our blog.
The Challenge of Enterprise Cyber Risk Management
Corporate assets are exposed to cyberthreats in almost every imaginable way.
The attack surface area is immense, including every endpoint, application, data store and infrastructure element. And, none of these are static as applications are constantly changing, with systems and hardware continuously being updated.
In practical terms, the challenges in enterprise cyber-risk management revolve around maintaining awareness and control in a massively complex and rapidly shifting environment.
Effective vulnerability management programmes automate the collection, correlation, and analysis of data from all relevant sources of vulnerability, asset, and business context to identify and prioritise risk.
This insight is then used to plan and implement human and machine actions designed to avoid, mitigate, or remediate risks.
A seamlessly integrated ecosystem helps vulnerability management programmes achieve these goals in an efficient, effective, and consistent manner.
Combining Brinqa and our best practices for an effective Vulnerability Management programme
Based upon extensive work with enterprise customers S4 Applications has compiled a list of eight best practice steps for vulnerability assessment and remediation solutions.
Read our blog Best Practice Steps for Effective Vulnerability Lifecycle Management
Overview of our 8 best practice steps for vulnerability management:
- Build repository for data
- Populate data on regular basis
- Manage automatic mitigation rules
- Understand risk
- Generate tickets for remediation
- Closing tickets
- Risk management
- Report on everything
Below we have combined our 8 best practice steps with Brinqa and it’s risk based vulnerability management features.
Step 1 – Build repository for data
You’ll want to hold information on every asset connected to the network, physical and virtual assets.
- The Brinqa data model has evolved over many years and is ready to hold data about all of your assets, physical and virtual.
- Utilise the Brinqa Knowledge Graph to integrate the various relevant data sources.
- Brinqa allows extensions to accommodate objects that are unique to a customer.
- Option to be extended by you or the Brinqa services team.
Step 2 – Populate data on regular basis
There are a number of different data source types that you can collect data from (150+ in Brinqa), connecting securely to the source. Not all data is directly available, and can be to be inferred from other data.
- Brinqa has a comprehensive set of maintained connectors, a full list is available here for review: https://www.brinqa.com/connectors/
- Has standard rules for dealing with things that most customers do, like differentiating external and internal (RFC 1918) addresses for example.
- Brinqa allows data to be inferred, using short code snippets, which makes it Infinitely flexible.
Step 3 Manage automatic mitigation rules
When issues (vulnerabilities) are found it is always best to remediate them; but this takes time.
There are many technologies from WAFs to networking equipment, that can give partial or full mitigation while the root cause is dealt with. Once the issue has been remediated then the temporary mitigation should be removed.
Brinqa has the ability to check for mitigations and as appropriate create tickets to get teams to implement them. When Brinqa finds that all issues have been remediated, it can then generate tickets to have the temporary mitigations removed.
Step 4 Understand risk
Now that everything is in one place, you can assign the risk based on several inputs. You can collate the information, drop it into an algorithm and score each vulnerability on each server uniquely.
- Brinqa have spent many years refining their risk scoring algorithm so that it works out of the box and implements best practise.
- The algorithm is available in source code form, and can be adjusted to your unique needs if desired.
Step 5 Generate tickets for remediation
Now that you can prioritise all vulnerabilities and other date data, you need to remediate the most important ones.
- Brinqa has a very sophisticated ticket creation engine.
- Rules can be defined and set in a hierarchy. This allows you to set precedence of rules and also drive multiple different ticketing engines at once (say ServiceNow for infrastructure issues and Jira for application issues).
Tickets also need to be grouped together in sensible ways. This varies by platform, but consider the most common (Windows), here a given patch may remediate many CVEs (vulnerabilities), so you want 1 ticket to apply the patch, not one per CVE.
Step 6 Closing tickets
When the patching teams have completed their work they usually move a ticket into a status similar to “Work Completed but not verified”. Brinqa can then trigger a re-scan if needed or just wait for the next scheduled scan.
When the re-scan occurs Brinqa will then fully close down the ticket. If it finds tickets that are flagged as above, but the scanner says are not fixed, then the ticket can be moved back to the patching team (typically to reboot or similar).
Great care is taken by Brinqa with this process because it is much more complex than it looks. Scanners don’t usually report that something is remediated, only that it is not still present, this means that examining the scope of the scan configuration is required before decisions about closing tickets can be made (for example, if Server S had vulnerability V last week, but on this week’s scan vulnerability V is not there; is that because V was remediated or was it a “Quick Scan” that didn’t check for V?).
Other decisions also need to be made around when a server is decommissioned, and what should happen to it’s tickets, and what should happen if it is recommissioned.
Step 7 Risk management
When an item has been flagged as a risk, there needs to be an approval process where specific mitigations are discussed and risks reviewed. If the business decides to accept the risk, then it should only be for a limited amount of time, and needs to be reviewed / accepted again.
Brinqa can help the remediation teams identify the issues and trigger the processes needed to drive the risk management process and also the review cycles.
Step 8 Report on everything
- Hundreds of reports available out of the box.
- Full security model so that users only see data about the servers they own / manage.
- User configurable reports and dashboards.
Next steps
Brinqa vulnerability management solutions.
Read more about risk based vulnerability management with our Brinqa case studies, learn more about Brinqa or contact S4 Applications to request a demo.
To learn more about vulnerability management, read out blog: Staying safe with Risk Based Vulnerability Management.